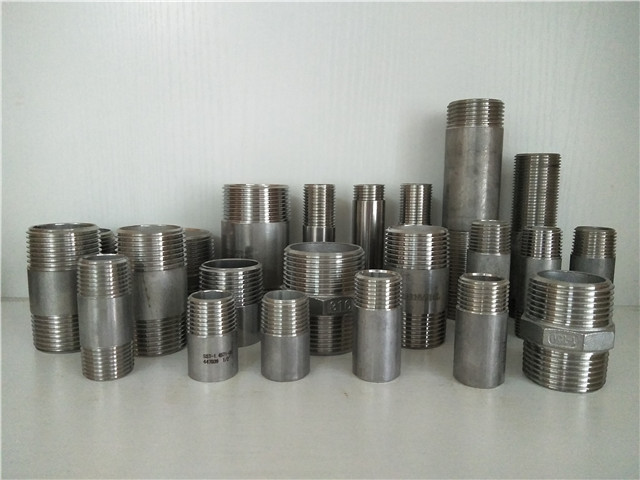
This passage mainly discusses thread standards of nipples and pipes in Europe, and I know you want to find your need quickly, so click the blue title to skip to the content that you need.
1. Pipe Nipples: Types and Thread Standards
(1) Types
(2) Standard
2. An Overview of Industrial Pipes
(1) Standard
(2) Thickness
(3) Extra Heavy
(1) Electric galvanized
(2) Hot-dipped galvanized
4. More information about long screw pipe
1. Pipe Nipples: Types and Thread Standards
(1) Types
-
Running nipple/close nipple
Running nipple, also known as close nipple features threaded sections that nearly encompass the entire nipple.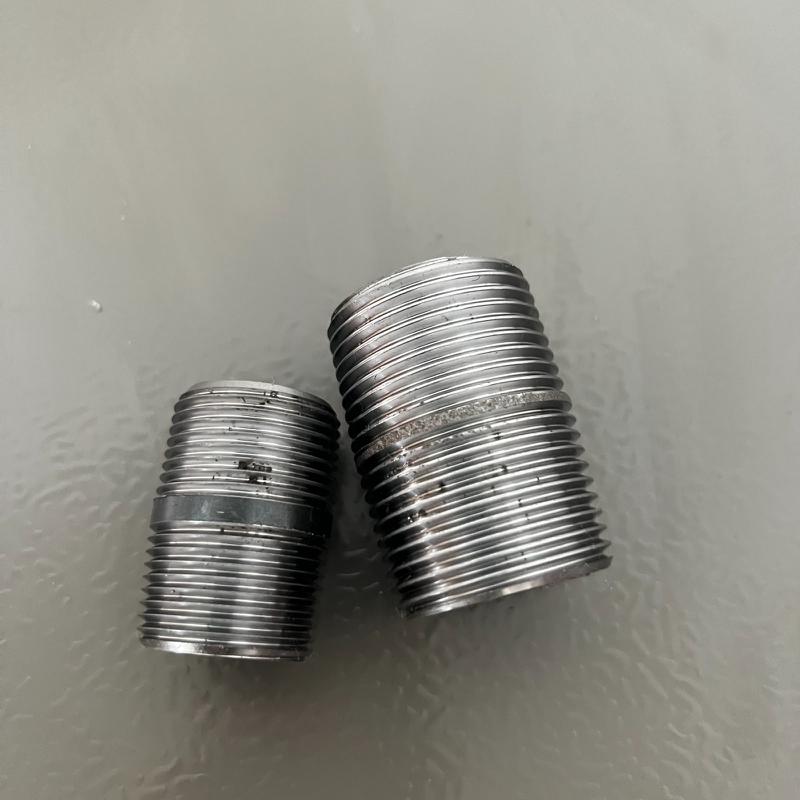 
The difference is that the running nipple exceeds the length of a standard nipple for closer nipple connections that can accommodate deeper piping; additionally, the length adjustment is flexible. But the close nipple is a very short pipe fitting with threads covering most of the fitting and a short unthreaded section in the center, usually used for two fittings or valves close connection to avoid too big a gap.
-
Long screw pipe nipple
The long screw pipe nipple is the running nipple but longer,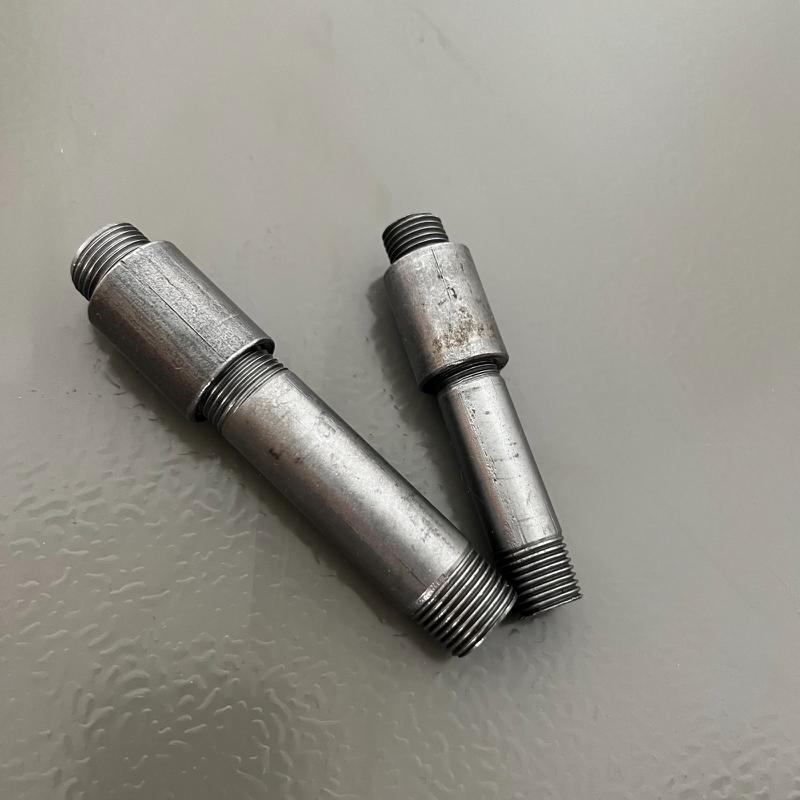 and the threaded part covers a large portion of the joint that offers more adjustment space when installation. It brings flexible choices for piping systems that need regulation within limits than normal nipples and have stability and adjustability. I will introduce specifically more information on the long screw pipe nipples and two thread standards in the last of the article.
and the threaded part covers a large portion of the joint that offers more adjustment space when installation. It brings flexible choices for piping systems that need regulation within limits than normal nipples and have stability and adjustability. I will introduce specifically more information on the long screw pipe nipples and two thread standards in the last of the article.
-
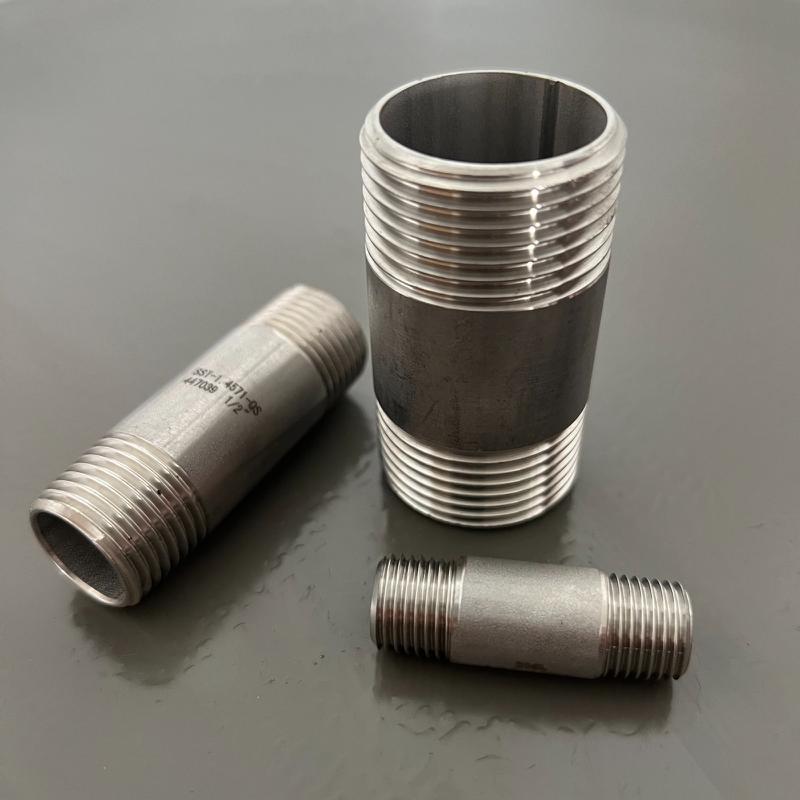 Barrel nipple
Barrel nipple
The barrel nipple is threaded on the two ends and unthreaded middle part, the whole is barrel-shaped and has strength and stability. They can connect stability and promote durability in plumbing systems used in construction piping, water systems, and the petrochemical industry.
-
Welded nipple
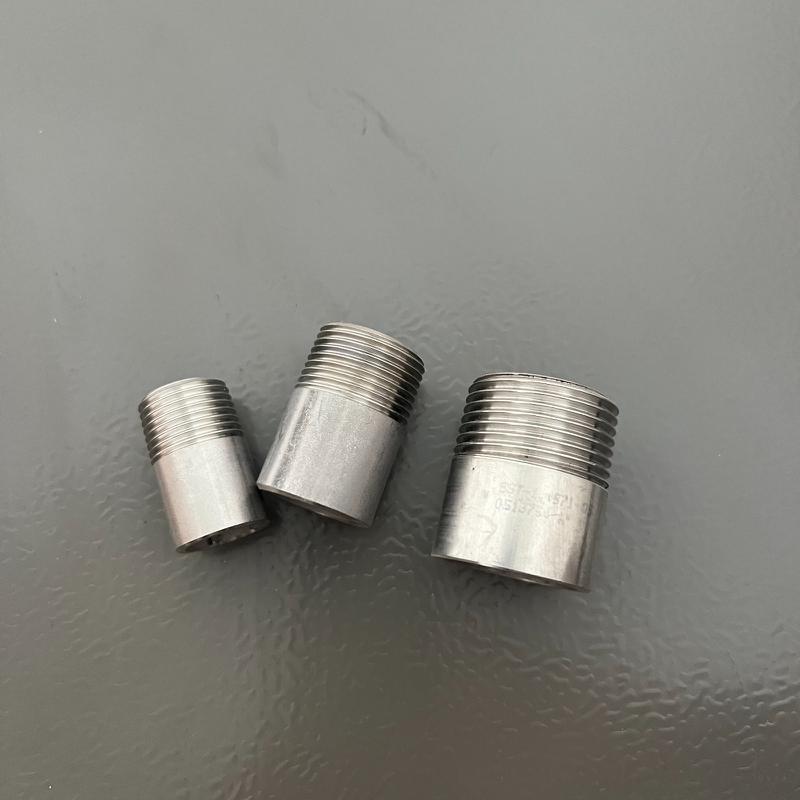 Welding nipples putting the nipples welded to other pipes or
Welding nipples putting the nipples welded to other pipes or
facilities to form a permanent connection, strip down, and replace the nipple by turning the thread ends at any time. It is permanent, firm, can withstand high pressure, leakproof, and widely used in high-pressure steam or oil pipelines and more high-pressure, temperature, and corrosivity environments.
-
Reducing hose nipple
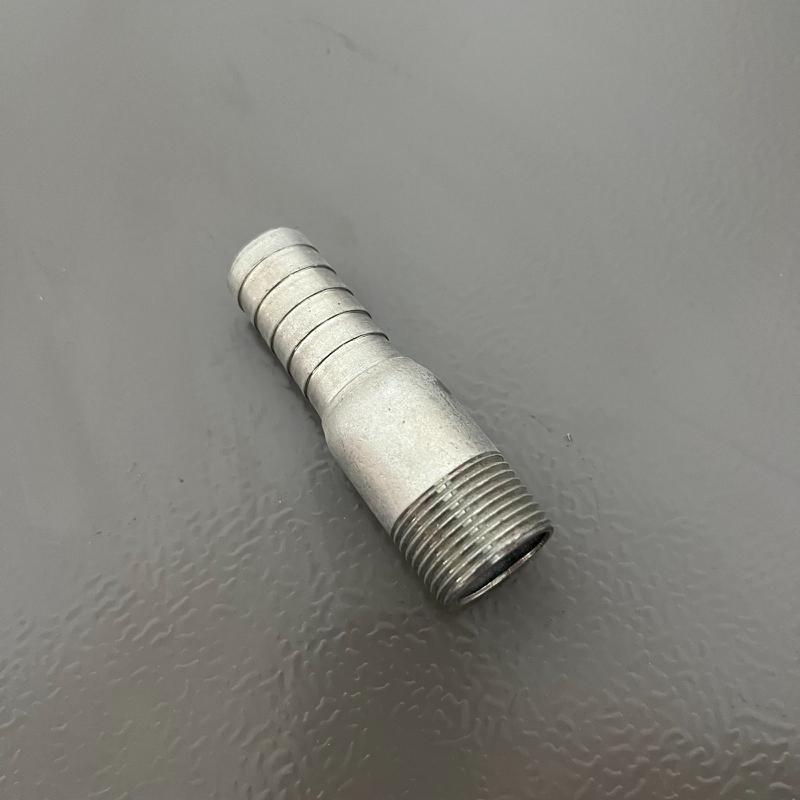

The reducing hose nipple has one large diameter
and one smaller diameter connector by the sides for pipelines and tube connections designed with varying diameters to transport liquids. This design facilitates convenient pressure and flow adjustments.
(2) Standard
Pipe nipples have a general standard and several thread standards. DIN2982 ensures interchangeability, reliability, and airtightness as a general standard, stipulating the design, manufacture, and examination requirements of nipples. DIN 2982 list detailed the standard diameter and screw pitch with male thread, including sizes demanded in different specifications to ensure the pipe nipple can be connected reliably with other fittings. DIN 2982 for material needs usually needs carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy to satisfy corrosion and strength in various environments.
Nipples have three common international tread standards that stipulate the types, sizes, connection types, and more of pipe thread.
-
DIN2999: German standard, popular in European countries, has certain airtightness for gas and liquid transportation in industrial applications.
-
BS21: This criterion comes from the British Standards Institution, which has two types of tapered thread(BSPT) and straight thread(BSPP), which is the thread that can form a good seal without gasket and sealing material.
-
ISO7-1: ISO7-1 is one international criterion that is universal and fit for various industrial and construction piping systems.

The above several standards have high compatibility and a similar design to ensure the normalization of thread connection globally.
2. An Overview of Industrial Pipes
(1) Standard
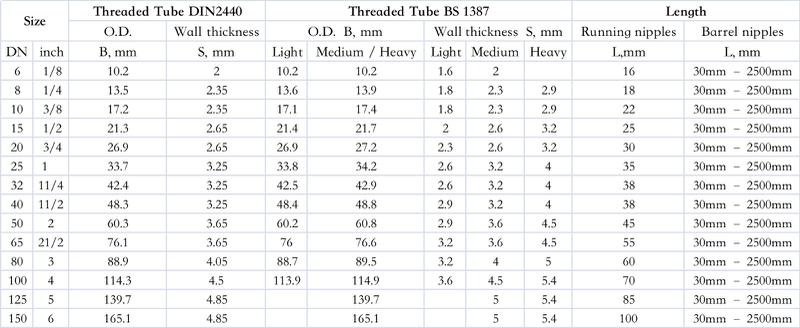
Pipes commonly have two standards, DIN2440 and BS1387, from Germany and Britain, through different standards to establish the produce, sizes, function, and more.
-
DIN2440: This criterion is common in gas and water transportation, HVAC, etc. The thickness range of DIN2440 pipes usually includes thinner to medium, designed medium and low-pressure applications.
-
BS1387: British criterion, suitable for water, gas, and more liquid transportation, light, medium, and heavy thick to meet needs in the different pressure applications.
(2) Thickness
The pipe has several kinds according to the different thicknesses, such as light, medium, and heavy. Thicker can withstand more pressure, and prices will rise along with the thick of the pipe. They each fit different high-pressure resistance, weight, and usage scenarios.
-
Light: The thickness of the light pipe is the thinnest pipe, such as schedule 10 or 20, suitable for low pressure and transport of liquid, commonly used in supplying water in-house, HVAC, and more light construction applications. It is lightweight, easy to install, and low-cost.
-
Medium: The thickness and strength of medium pipe are moderate, between the light pipe and heavy pipe. It is suitable for moderate temperature and pressure of liquid transportation, such as industry engineering, construction industry, gas transport, etc. High cost-effective, fit for multiple applications.
-
Heavy: The thickness of heavy pipes is thicker than the first two, which can withstand higher pressure and temperature, generally referring to schedule 80 or more thick pipes. They can applied in high-pressure environments such as the chemical industry, gas transportation, and steam systems. Due to their strength and durability, they can used in boiler tubes and high-pressure gas plumbing and offer high strength and safety in harsh environments.
(3) Extra-heavy pipe
A particular thickness refers to schedule 160 or higher and is designed for employment in extreme environments. It has very high intensity and durability and is fit for nuclear power stations, deep-sea drilling, high-pressure steam pipelines, etc.
Click here to select suitable pipes for your industry and more information you need!
3. Surface technics
(1) Electric galvanized
Thin, glossy coatings with low corrosion resistance are suitable for dry environments. It is fit for use in dry environments. It is less costly and has an attractive appearance.
(2) Hot-dipped galvanized
Hot-dipped galvanized forms a thicker and better corrosion resistance that can withstand outdoor and harsh environments. The appearance is average, but the performance is superior.
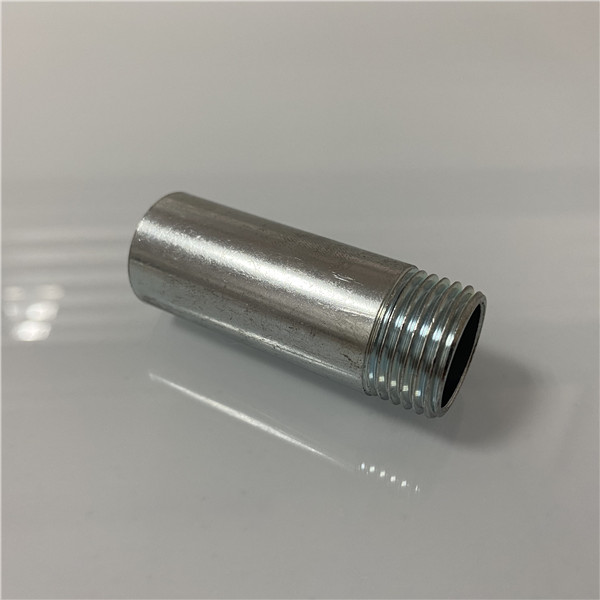
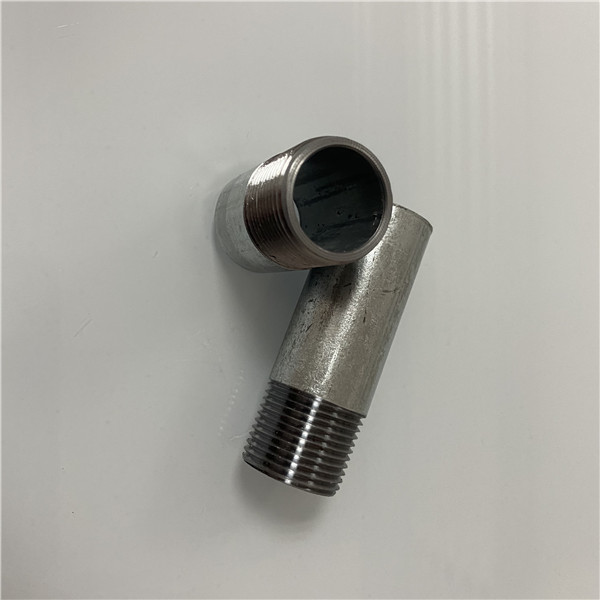


Choose hot-dipped galvanized fittings for long-term use and applications requiring high corrosion resistance, while electro-galvanized is less costly and affordable for short-term, environmentally friendly applications.
4. More information about long screw pipe
Introduce several standards with long screw pipes in the following they all conform to ISO7-1 standard.
(1) Parallel thread
This means that the outer and inner diameters of the threaded portion are equal, and the diameter does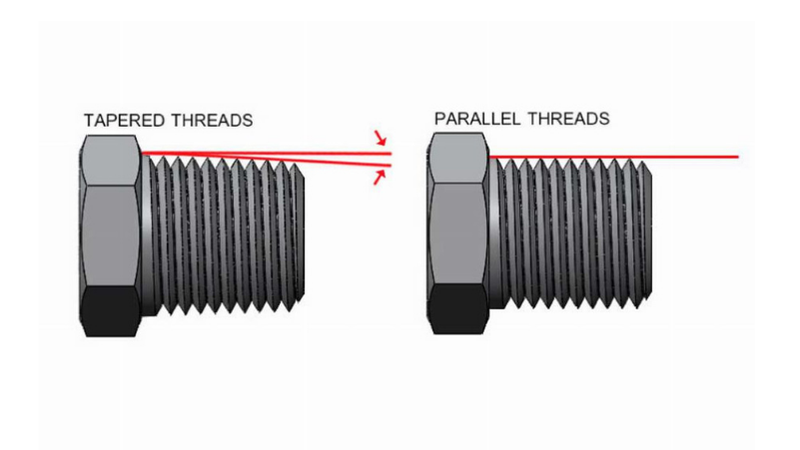 not change when the thread rotation is fit for low pressure and detachable connection.
not change when the thread rotation is fit for low pressure and detachable connection.
(2) Taper thread
Usually, the diameter of one end is larger than the other, creating a better seal when connected and withstand high temperature or pressure environments.
(3) Cylinder thread
The alternate name G Thread conforms to DIN 259 and is a 55-degree non-threaded sealed pipe thread, with good sealing and compatibility. The same outside diameter at both ends is suitable for connection with other parallel threaded fittings. G thread is ideal for industrial applications and transporting fluids and gases for conveying liquids and gases. Generally, the sealing effect depends on accuracy, material, and installation of the compact degree of G thread.





